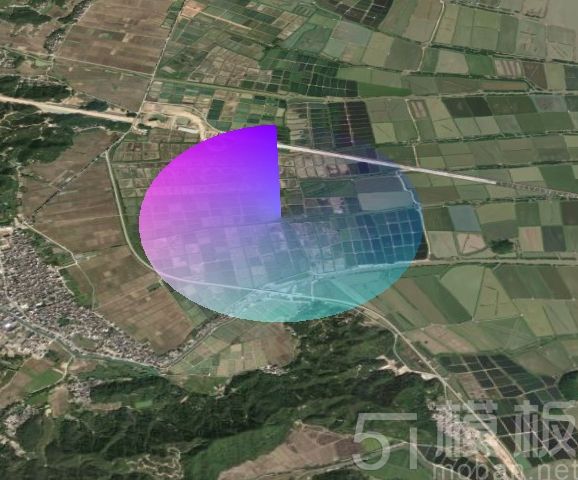
cesium实现雷达扫描图,效果图如下:
1、安装gsap,这个是为了动画效果
npm install gsap
2、新建RadarMaterialProperty.js文件,这个主要是雷达图的材质,代码如下:
import * as Cesium from "cesium";
import gsap from "gsap";
export default class RadarMaterialProperty {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
this.definitionChanged = new Cesium.Event();
Cesium.Material._materialCache.addMaterial("RadarMaterial", {
fabric: {
type: "RadarMaterial",
uniforms: {
uTime: 0,
},
source: `
czm_material czm_getMaterial(czm_materialInput materialInput)
{
// 生成默认的基础材质
czm_material material = czm_getDefaultMaterial(materialInput);
// 旋转uv
vec2 newSt = mat2(
cos(uTime),-sin(uTime),
sin(uTime),cos(uTime)
)*(materialInput.st-0.5);
newSt = newSt+0.5;
// 获取st
vec2 st = newSt;
// 设置圆,外部透明,内部不透明
float alpha = 1.0 - step(0.5,distance(st,vec2(0.5))) ;
// 按照角度来设置强弱
float angle = atan(st.x-0.5,st.y-0.5);
// angle是从-pi到pi的,所以如果要设置从0-1的转变,需要加上pi
float strength = (angle+3.1416)/6.2832;
// 将强弱与透明度结合
alpha = alpha*strength;
material.alpha = alpha;
material.diffuse = vec3(st.x,st.y,1.0);
return material;
}
`,
},
});
this.params = {
uTime: 0,
};
gsap.to(this.params, {
uTime: 6.28,
duration: 1,
repeat: -1,
ease: "linear",
});
}
getType() {
// 返回材质类型
return "RadarMaterial";
}
getValue(time, result) {
result.uTime = this.params.uTime;
// 返回材质值
return result;
}
equals(other) {
// 判断两个材质是否相等
return other instanceof RadarMaterialProperty && this.name === other.name;
}
}3、使用
// 导入雷达材质文件
import RadarMaterialProperty from './lib/RadarMaterialProperty'
// 将椭圆添加雷达材质,并贴地:
let rader = viewer.entities.add({
position: Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(113, 22),
name: '雷达扫描',
ellipse: {
semiMajorAxis: 1000,
semiMinorAxis: 1000,
material: new RadarMaterialProperty('雷达图'),
height: 60,
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.RELATIVE_TO_GROUND,
}
})
viewer.flyTo(rader)4、如果觉得颜色太绚丽,可以使用下面的着色器代码替换上面的代码,同时支持传入颜色和速度:
import * as Cesium from "cesium";
import gsap from "gsap";
export default class RadarMaterialProperty {
constructor(name, color, speed) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
this.speed = speed
this.definitionChanged = new Cesium.Event();
Cesium.Material._materialCache.addMaterial("RadarMaterial", {
fabric: {
type: "RadarMaterial",
uniforms: {
color: this.color,
speed: this.speed
},
source: `
uniform vec4 color;
uniform float speed;
#define PI 3.14159265359;
czm_material czm_getMaterial(czm_materialInput materialInput){
czm_material material = czm_getDefaultMaterial(materialInput);
vec2 st = materialInput.st;
vec2 scrPt = st * 2.0 - 1.0;
float time = czm_frameNumber * speed / 1000.0 ;
vec3 col = vec3(0.0);
mat2 rot;
float theta = -time * 1.0 * PI - 2.2;
float cosTheta, sinTheta;
cosTheta = cos(theta);
sinTheta = sin(theta);
rot[0][0] = cosTheta;
rot[0][1] = -sinTheta;
rot[1][0] = sinTheta;
rot[1][1] = cosTheta;
vec2 scrPtRot = rot * scrPt;
float angle = 1.0 - (atan(scrPtRot.y, scrPtRot.x) / 6.2831 + 0.5);
float falloff = length(scrPtRot);
material.alpha = pow(length(col + vec3(.5)),5.0);
material.diffuse = (0.5 + pow(angle, 2.0) * falloff ) * color.rgb;
return material;
}
`,
},
});
this.params = {
uTime: 0,
};
gsap.to(this.params, {
uTime: 6.28,
duration: 1,
repeat: -1,
ease: "linear",
});
}
getType() {
// 返回材质类型
return "RadarMaterial";
}
getValue(time, result) {
result.uTime = this.params.uTime;
// 返回材质值
return result;
}
equals(other) {
// 判断两个材质是否相等
return other instanceof RadarMaterialProperty && this.name === other.name;
}
}5、使用的时候多传个颜色和动画速度:
let rader = viewer.entities.add({
position: Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(113, 22),
name: '雷达扫描',
ellipse: {
semiMajorAxis: 1000,
semiMinorAxis: 1000,
material: new RadarMaterialProperty('雷达图', Cesium.Color.YELLOW, 20),
height: 60,
heightReference: Cesium.HeightReference.RELATIVE_TO_GROUND,
}
})